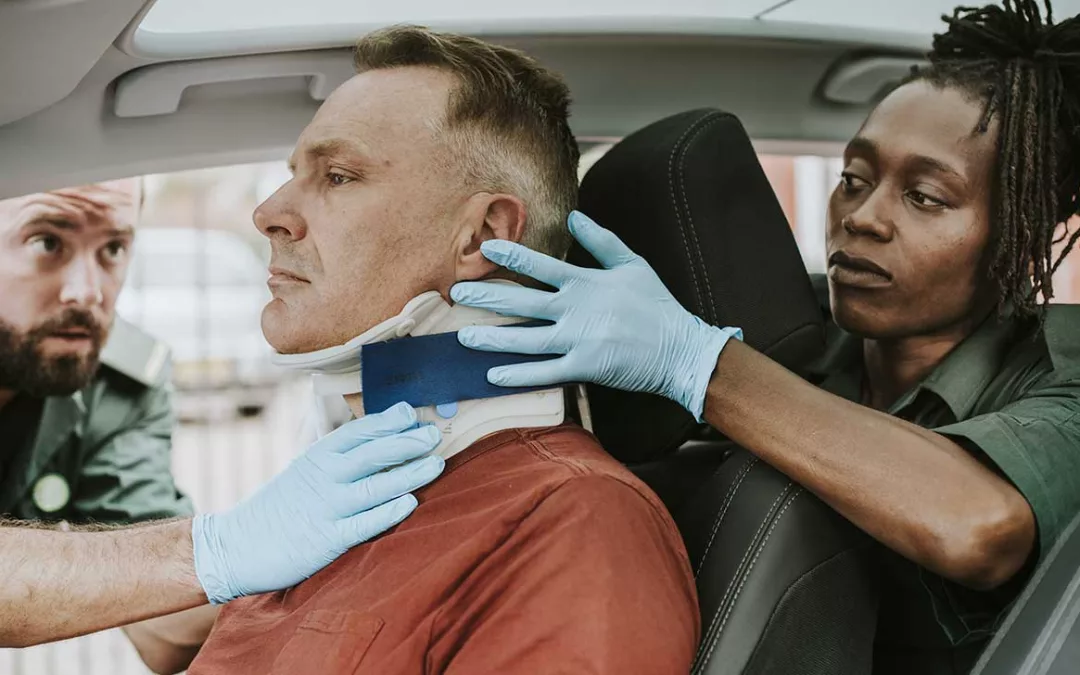
The Journey to Recovery: Understanding How Long Whiplash Lasts
Whiplash is a common injury resulting from the sudden and forceful back-and-forth motion of the head and neck. Often associated with car accidents, whiplash can also occur during sports, slips, and falls, or other unexpected events. While it is a relatively common injury, there is no one-size-fits-all answer to the question, “How long does whiplash last?” The duration of whiplash and the journey to recovery can vary significantly from person to person. In this comprehensive blog post, we’ll explore the various aspects of whiplash, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and, most importantly, the factors influencing its duration.
What is Whiplash?

Whiplash is a type of neck injury that occurs when the head is suddenly and forcefully jerked backward and then forward, creating a whip-like motion. This rapid and violent movement can strain and damage the soft tissues, muscles, ligaments, tendons, and other structures in the neck. Whiplash is often associated with motor vehicle accidents, particularly rear-end collisions, but it can also result from various other situations and activities.
The key characteristics of whiplash include:
- Sudden and Forceful Motion: Whiplash is typically caused by a sudden and forceful back-and-forth motion of the head and neck. This motion can be caused by the impact of a collision, a fall, or another unexpected event.
- Damage to Soft Tissues: The primary source of injury in whiplash is damage to the soft tissues of the neck. This can include overstretching or tearing of muscles and ligaments, resulting in pain and inflammation.
- Variable Symptoms: Symptoms of whiplash may not appear immediately after the injury and can vary in intensity. Common symptoms include neck pain, stiffness, headaches, shoulder pain, and, in some cases, arm weakness or numbness. Cognitive and emotional symptoms, such as difficulty concentrating and irritability, can also occur.
- Delayed Onset: Whiplash symptoms may take hours or even days to develop after the traumatic event, which can make it challenging to connect the symptoms to the injury.
- Range of Severity: Whiplash injuries can range from mild to severe, depending on the force of the impact and the individual’s physical condition. In some cases, whiplash may also result in damage to the spine, discs, and nerves.
While whiplash is often associated with car accidents, it can occur in various other situations, including sports injuries, slip and fall accidents, physical abuse, and amusement park rides. The symptoms and severity of whiplash can vary from person to person, and the duration of recovery may depend on multiple factors, such as the severity of the injury, age, pre-existing conditions, and compliance with treatment. Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential for managing and recovering from whiplash injuries.
Causes of Whiplash

Whiplash is typically caused by a sudden and forceful back-and-forth motion of the head and neck, which strains the soft tissues and structures in the neck. The most common cause of whiplash is motor vehicle accidents, but it can also result from various other situations and activities. Here are some of the primary causes of whiplash:
- Motor Vehicle Accidents: Car accidents are the most frequent cause of whiplash. This can happen when one vehicle is rear-ended by another, causing the occupants’ heads to jerk forward and then suddenly snap back.
- Sports Injuries: High-impact or collision sports like football, rugby, and ice hockey can lead to whiplash injuries. Players can experience neck trauma during tackles, collisions, or falls.
- Slip and Fall Accidents: A slip and fall, especially when the head is jolted abruptly, can result in whiplash. Falling backward or forward can cause the head and neck to move suddenly.
- Physical Assault: Whiplash can occur due to physical abuse or assault when the head is forcefully shaken or hit.
- Amusement Park Rides: Rollercoasters and other amusement park rides that subject riders to sudden, forceful movements can sometimes cause whiplash injuries, particularly if the head and neck are not properly supported.
- Workplace Accidents: Some workplace accidents, such as those involving heavy machinery or equipment, can lead to whiplash if the head and neck are subjected to rapid and unexpected movements.
- Recreational Activities: Activities like horseback riding, skiing, or snowboarding can also result in whiplash if a person falls or collides with an object.
- Cycling Accidents: Cyclists involved in accidents, especially when they are thrown off their bikes, can experience whiplash injuries.
- Shaken Baby Syndrome: Infants can suffer from whiplash-like injuries if they are shaken violently, which can result in severe neck and head trauma.
It’s important to note that whiplash injuries are not always immediately apparent. Symptoms may take hours or even days to develop after the initial traumatic event. Additionally, the severity of whiplash can vary from mild to severe, depending on the force of the impact and the individual’s physical condition. If you suspect you have whiplash or have been involved in an accident that could cause it, it’s essential to seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Symptoms of Whiplash

Whiplash is characterized by a range of symptoms that typically develop after a sudden and forceful back-and-forth motion of the head and neck. These symptoms may vary in intensity and onset time, and not all individuals with whiplash will experience all of them. Common symptoms of whiplash include:
- Neck Pain: Neck pain is one of the most prevalent and prominent symptoms of whiplash. The pain is usually located in the neck area and may range from mild to severe.
- Neck Stiffness: Individuals with whiplash often experience a noticeable decrease in neck flexibility, resulting in stiffness and difficulty moving the head.
- Headaches: Whiplash can lead to headaches, often referred to as cervicogenic headaches, which are caused by neck pain and muscle tension.
- Shoulder Pain: Pain and discomfort in the shoulders and upper back are common symptoms of whiplash due to the forceful movement of the head and neck.
- Arm Weakness or Numbness: In more severe cases, whiplash can affect the nerves in the neck, leading to arm weakness or numbness.
- Dizziness: Some individuals with whiplash experience dizziness, which can result from the injury’s impact on the nervous system.
- Fatigue: Whiplash may lead to feelings of fatigue, likely due to the body’s response to pain and the healing process.
- Cognitive and Emotional Symptoms: Whiplash can affect cognitive functions and emotions. Common cognitive symptoms include memory problems and difficulty concentrating. Emotional symptoms may include irritability, mood swings, and increased stress or anxiety.
- Tinnitus (Ringing in the Ears): Some people with whiplash report tinnitus, which is a ringing or buzzing sound in the ears.
- Jaw Pain: Whiplash can lead to jaw pain, particularly if the jaw is jolted during the traumatic event.
- Sleep Disturbances: Sleep disturbances, including difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, can be related to whiplash pain and discomfort.
- Visual Disturbances: Some individuals may experience visual disturbances, such as blurred vision or difficulty focusing on objects.
- Difficulty Swallowing: Swallowing difficulties may occur in some cases, although this is less common.
It’s important to note that whiplash symptoms may not become immediately apparent following the injury. They can develop within hours or even days after the traumatic event. If you experience any of these symptoms following an accident or injury, it’s crucial to seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention can help manage symptoms and improve the chances of a smoother and faster recovery.
Diagnosing Whiplash

Diagnosing whiplash typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and, in some cases, imaging studies to rule out other potential injuries. A healthcare provider will follow a systematic approach to determine if an individual has suffered from whiplash. Here’s how the diagnosis is typically conducted:
- Medical History:
- The healthcare provider will begin by taking a detailed medical history from the patient. This history will include information about the accident or incident that caused the injury, the mechanism of injury, and the patient’s symptoms.
- The patient will be asked about the location, quality, and severity of their pain, as well as any other symptoms they may be experiencing, such as headaches, dizziness, or numbness.
- Physical Examination:
- The healthcare provider will perform a physical examination to assess the patient’s range of motion, neck tenderness, and neurological function.
- The range of motion of the neck is typically assessed by having the patient move their head in various directions, checking for any limitations or pain during movement.
- The healthcare provider will palpate the neck and surrounding areas to identify areas of tenderness or muscle spasm.
- Neurological function will be assessed to check for any signs of nerve involvement. This may involve testing reflexes, muscle strength, and sensation in the arms and hands.
- Imaging Studies (if necessary):
- In most cases, a diagnosis of whiplash can be made based on the medical history and physical examination. However, in some situations, imaging studies may be recommended to rule out other potential injuries or to assess the severity of the whiplash.
- X-rays: X-rays are used to check for fractures, dislocations, or other bony injuries in the neck. While whiplash primarily involves soft tissues, fractures or dislocations can occur, especially in more severe cases.
- CT Scans: Computed tomography (CT) scans can provide more detailed images of the neck and are often used to assess the spine and soft tissues for any structural abnormalities.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI is a highly sensitive imaging technique that can help visualize soft tissues, including muscles, ligaments, and discs in the neck. It can be particularly useful in identifying soft tissue injuries that may not be visible on X-rays or CT scans.
It’s important to note that the absence of visible abnormalities on imaging studies does not rule out whiplash, as whiplash primarily involves damage to the soft tissues. The diagnosis is based on the combination of the mechanism of injury, the patient’s reported symptoms, and the findings of the medical history and physical examination.
Once diagnosed, appropriate treatment can be initiated to manage the symptoms and promote the recovery of individuals with whiplash. Treatment options may include rest, medications, physical therapy, and other therapeutic approaches to relieve pain and restore neck function.
Whiplash Treatment

The treatment of whiplash is typically aimed at relieving pain, reducing inflammation, promoting healing, and restoring the function of the neck. The specific treatment plan may vary depending on the severity of the injury, the individual’s symptoms, and their overall health. Here are the common treatment options for whiplash:
- Rest and Activity Modification:
- Rest is often the initial treatment for whiplash to prevent further damage and allow the injured tissues to heal.
- The patient is advised to avoid activities and movements that exacerbate their symptoms, such as heavy lifting, strenuous physical activities, and activities that require extensive neck movement.
- Medications:
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter or prescription pain medications like acetaminophen or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be recommended to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
- Muscle Relaxants: These medications can help relax tense muscles and reduce muscle spasms that may be contributing to neck pain.
- Prescription Pain Medications: In more severe cases, the healthcare provider may prescribe stronger pain medications.
- Physical Therapy:
- Physical therapy is a key component of whiplash recovery. A physical therapist will design a treatment plan that includes exercises and stretches to:
- Strengthen the neck and upper back muscles.
- Improve range of motion and flexibility in the neck.
- Correct poor posture and promote proper alignment.
- Physical therapy is a key component of whiplash recovery. A physical therapist will design a treatment plan that includes exercises and stretches to:
- Heat and Cold Therapy:
- Heat and cold therapy can help alleviate pain and inflammation.
- Heat therapy, such as warm compresses or heating pads, is often applied before physical therapy exercises to relax and loosen tissues.
- Cold therapy, like ice packs, can be applied to reduce inflammation and numb the affected area.
- Neck Collars:
- In some cases, a soft cervical collar may be recommended for a short period to support the neck and reduce motion. However, the use of collars for extended periods is generally discouraged, as they can weaken the neck muscles and slow down recovery.
- Injections:
- Corticosteroid injections: These may be administered directly into the affected area to reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief from pain.
- Alternative Therapies:
- Chiropractic Care: Chiropractors can provide adjustments and manual therapy to help relieve pain and improve neck function.
- Acupuncture: Some individuals find relief from whiplash symptoms through acupuncture.
- Massage Therapy: Massage can help relax tense muscles and improve blood flow to the injured area.
- Psychotherapy:
- In cases where whiplash leads to cognitive and emotional symptoms, psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can help individuals cope with the psychological impact of the injury.
- Self-Care:
- Patients are often encouraged to practice self-care techniques, such as gentle neck exercises and maintaining good posture, to aid in their recovery and prevent further injury.
- Gradual Return to Normal Activities:
- As the symptoms improve, individuals can gradually return to their normal activities, including work and exercise, under the guidance of their healthcare provider or physical therapist.
It’s important for individuals with whiplash to follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations and treatment plan. Compliance with treatment and active participation in rehabilitation exercises are critical for a successful recovery. In most cases, whiplash symptoms improve over time, and with the right approach, many individuals can expect to fully recover within a reasonable timeframe. However, the duration of recovery may vary based on the severity of the injury and individual factors.
Factors Influencing Whiplash Recovery

The duration and success of whiplash recovery can vary significantly from person to person and depend on various factors. Understanding these factors is essential for healthcare providers and individuals with whiplash to manage expectations and tailor treatment plans. Here are the key factors that influence whiplash recovery:
- Severity of the Injury:
- The severity of the whiplash injury, including the extent of tissue damage and nerve involvement, can significantly impact the recovery timeline. More severe injuries may take longer to heal.
- Age:
- Age plays a role in recovery. Younger individuals often recover more quickly than older adults, as their bodies have better regenerative capabilities.
- Pre-Existing Conditions:
- Individuals with pre-existing neck or spinal conditions may experience prolonged recovery times due to the added complexity of their injuries.
- Prompt Diagnosis and Treatment:
- Early diagnosis and timely treatment can accelerate the recovery process. Delayed diagnosis and treatment may lead to chronic symptoms.
- Compliance with Treatment:
- Patient compliance with recommended treatments, including physical therapy and self-care, can greatly affect recovery. Individuals who actively participate in their rehabilitation plan tend to recover more effectively.
- Lifestyle Factors:
- Factors such as smoking, poor nutrition, and lack of exercise can slow down the healing process. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition and regular exercise, can promote faster recovery.
- Psychological Factors:
- Psychological factors like anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder can amplify the perception of pain and delay recovery. Addressing these issues through psychotherapy is essential for a comprehensive recovery plan.
- Legal and Insurance Issues:
- Legal and insurance matters, such as ongoing claims and disputes, can add stress and complexity to the recovery process. The resolution of these issues can impact the overall well-being of the injured individual.
- Support System:
- A strong support system, including friends and family, can positively influence recovery by providing emotional and practical assistance. Social support can help individuals cope with the physical and psychological challenges of whiplash.
- Work and Daily Activities:
- The nature of a person’s work and daily activities can impact recovery. Jobs that involve heavy physical labor or repetitive neck movements may require workplace modifications or temporary job changes to support recovery.
- Healthcare Access:
- Access to quality healthcare and specialized medical professionals can make a difference in the quality of care and, consequently, recovery outcomes.
- Overall Health and Nutrition:
- General health and nutrition play a role in recovery. Individuals who are in good overall health and maintain a balanced diet may recover more efficiently.
- Adaptive Strategies:
- Learning and implementing adaptive strategies can help individuals with persistent symptoms better manage their condition. These strategies may involve modifying daily activities or using assistive devices to reduce strain on the neck.
Understanding the interplay of these factors is critical in managing whiplash recovery. Healthcare providers can assess individual circumstances and develop personalized treatment plans, while individuals with whiplash can make informed decisions to support their recovery journey. Patience and persistence are key, as recovery from whiplash can be a gradual process, and the timeline may vary for each person.
Recovery Timeline for Whiplash
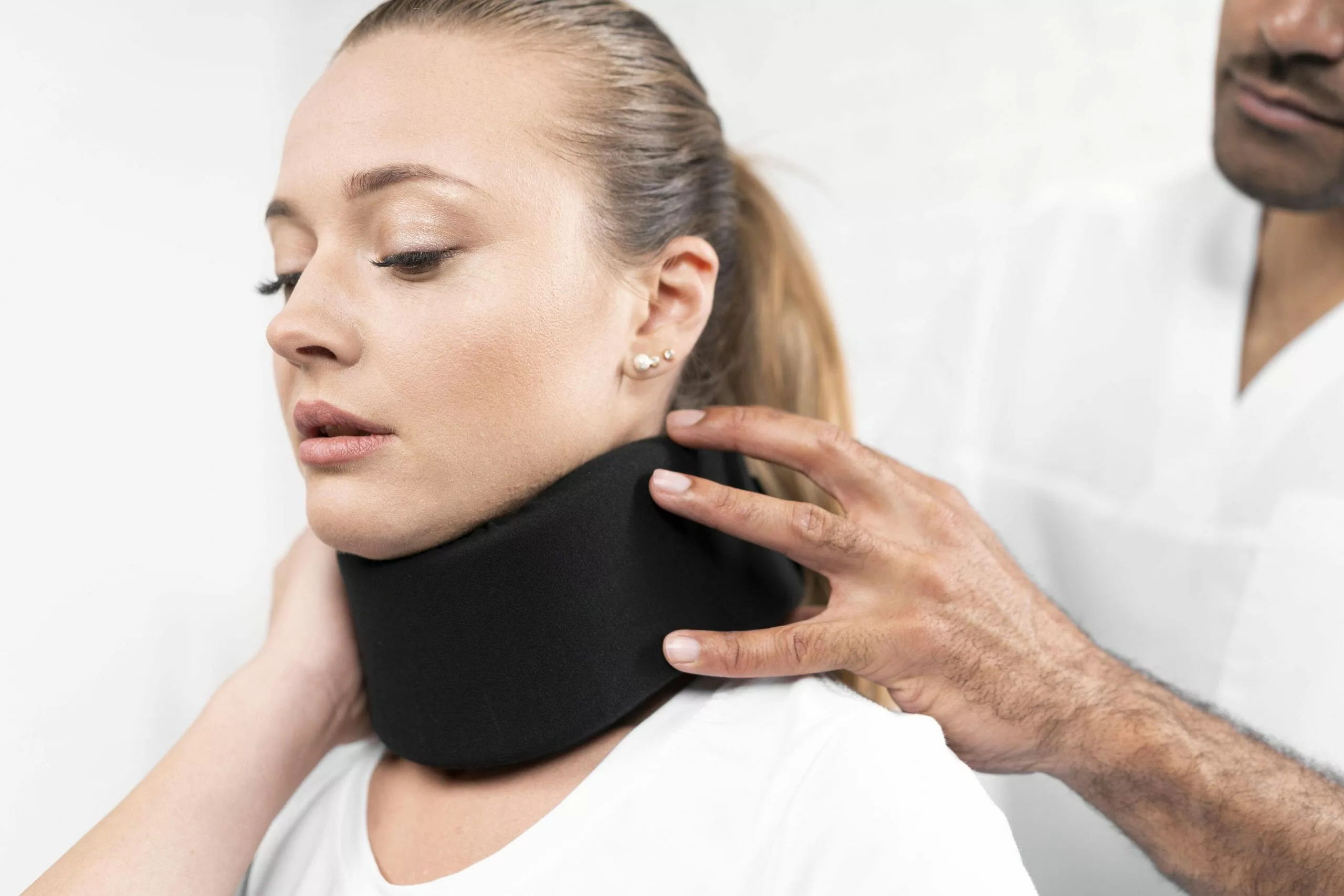

The recovery timeline for whiplash can vary widely among individuals and is influenced by several factors, including the severity of the injury, age, pre-existing conditions, compliance with treatment, and overall health. While some people may recover relatively quickly, others may experience prolonged symptoms. Here is a general timeline for whiplash recovery, but it’s essential to keep in mind that individual experiences may differ:
- Week 1-2:
- During the first week or two, individuals with whiplash typically experience acute symptoms. Pain and stiffness may be at their peak during this period.
- Rest is often essential during this phase to prevent further injury, and individuals are advised to avoid activities that exacerbate their symptoms.
- Week 2-6:
- Most people experience a noticeable reduction in symptoms during weeks 2 to 6. Pain and stiffness start to diminish.
- Physical therapy and self-care measures become increasingly important during this phase to improve neck flexibility and strength.
- Months 3-6:
- Many individuals continue to see improvements in their symptoms, with pain and discomfort diminishing further.
- Some people may return to work or resume their normal daily activities during this period.
- Months 6-12:
- A significant number of individuals recover fully within six to twelve months. For others, mild symptoms may persist but become manageable with self-care and occasional therapy.
- People can usually return to most of their pre-injury activities by this stage.
- Beyond 1 Year:
- A small percentage of individuals may experience chronic whiplash symptoms lasting longer than a year. In these cases, a more multidisciplinary approach involving pain management, psychological support, and adaptive strategies may be necessary.
- The focus may shift from trying to fully resolve symptoms to learning how to manage and live with them.
It’s important to remember that this timeline is a general guideline and not an absolute rule. Recovery from whiplash can be highly individual, and some people may recover more quickly, while others may take longer. Factors such as the severity of the injury, age, overall health, and compliance with treatment play a significant role in determining the timeline.
Patients should work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that suits their specific needs and monitor their progress throughout the recovery process. Additionally, patience and perseverance are key, as full recovery from whiplash can be a gradual journey, and it may require ongoing effort and support.
How to Prevent Whiplash?
Preventing whiplash is an important aspect of personal safety, and there are several measures and precautions you can take to reduce the risk of sustaining this injury. Whether you’re driving, playing sports, or engaging in various activities, these preventive strategies can help minimize the chances of experiencing whiplash:
- Proper Use of Seatbelts:
- Always wear your seatbelt when driving or riding in a motor vehicle. Proper seatbelt use can prevent your body from moving excessively during a collision, reducing the risk of whiplash.
- Adjusting Headrests:
- Ensure that the headrest of your vehicle is properly adjusted to align with the back of your head. This can provide support to your neck in the event of a rear-end collision.
- Safe Driving Practices:
- Follow safe driving practices, maintain a safe following distance, and avoid tailgating to reduce the risk of rear-end collisions.
- Vehicle Safety Features:
- Choose vehicles equipped with advanced safety features, such as headrests, seatbelt pretensioners, and airbags. These features can help minimize the effects of a collision.
- Proper Positioning in Vehicles:
- Sit upright in your seat with your back against the seatback and your head against the headrest. Avoid slouching or leaning forward while driving.
- Defensive Driving:
- Practice defensive driving by staying alert, obeying traffic laws, and anticipating potential hazards on the road. Being a cautious driver can help you avoid accidents.
- Sports Safety Equipment:
- If you participate in high-impact or collision sports, make sure to wear appropriate safety gear and equipment, including helmets and protective padding.
- Training and Technique:
- In sports and physical activities, focus on proper technique and body mechanics to reduce the risk of falls or collisions that could lead to whiplash.
- Falls Prevention:
- Take precautions to prevent falls, such as wearing appropriate footwear, keeping walkways clear of obstacles, and using handrails when available.
- Safe Workplace Practices:
- If you work in an environment where whiplash injuries are a risk, follow safety protocols and use proper equipment to reduce the chances of an accident.
- Educational Programs:
- Stay informed about the potential risks and causes of whiplash and educate yourself and your family about safety measures and accident prevention.
- Regular Exercise and Strength Training:
- Engaging in regular physical activity can help maintain strength and flexibility in your neck and upper body, which may reduce the risk of injury during accidents or falls.
- Avoiding Distracted Driving:
- Avoid using your phone or other distractions while driving. Distracted driving can lead to accidents and increase the risk of whiplash.
- Proper Lifting Techniques:
- When lifting heavy objects, use proper lifting techniques to reduce the risk of straining your neck and back.
- Regular Health Check-ups:
- Regular medical check-ups and maintaining good overall health can improve your ability to recover from injuries, should they occur.
Preventing whiplash is primarily about awareness, responsible behavior, and taking steps to reduce your exposure to risk. By practicing these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the chances of sustaining a whiplash injury in various situations and activities.
Conclusion: How Long Does Whiplash Last?
Whiplash is a complex and variable injury that affects individuals differently. The duration of whiplash recovery depends on numerous factors, including the severity of the injury, age, pre-existing conditions, and compliance with treatment. Understanding these factors and following a comprehensive treatment plan can help individuals on their journey to recovery. It’s essential for those who have experienced whiplash to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. With the right approach and support, the majority of individuals with whiplash can look forward to a full recovery within a reasonable timeframe.
BEST CHIROPRACTOR NEAR ME IN ORLANDO, FLORIDA
CALL NOW +1-407-434-7246
If you have suffered any type of injury or have been experiencing pain that just won’t go away regardless of what you do, then all you have to do is call and speak with our friendly staff. Find Best Chiropractic Care in Orlando, Florida. Our team can help you get the treatment you need and ensure that the pain you experience is alleviated – once and for all.
We are proud to serve the areas of Orlando, Altamonte Springs, Haines City, Plant City, Kissimmee, Winter Haven, and Ocala.
Contact us for Chiropractor near me in Orlando, Florida for an Appointment Today.
How do I know if my whiplash is serious?
You should see a doctor after an auto crash or other injury event, or if you have the following symptoms: pain or stiffness in the neck that goes away and then comes back. severe neck pain. pain, numbness, or tingling in your shoulders, arms, or legs.
Does whiplash go away by itself?
Most people who have whiplash feel better within a few weeks and don't seem to have any lasting effects from the injury. However, some people continue to have pain for several months or years after the injury occurred. It is difficult to predict how each person with whiplash may recover.
What is the best treatment for whiplash?
Most whiplash gets better with home care. Your doctor may advise you to take medicine to relieve pain or relax your muscles. You may suggest exercise and physiotherapy to increase flexibility and relieve pain. You can try wearing a neck (cervical) collar to support your neck.
Is it ok to massage whiplash?
Is it ok to massage a whiplash injury? Again, the short answer is yes, if your therapist is using the correct approach. The best option for recovery is a combination of experience, and therapeutic appropriate techniques that have been shown to work when studied by scientists.
What happens if whiplash goes untreated?
Untreated whiplash can trigger symptoms of degenerative disc disease that previously went unnoticed. Discs between spinal vertebrae usually act as shock absorbers and help bend the back. Still, with degenerative disc disease, the discs are worn down and offer less protection from injury and movement.



